Environmental, Social and Governance criteria are used by socially-conscious investors and shareholders to screen investments and assess a company's impact on the world

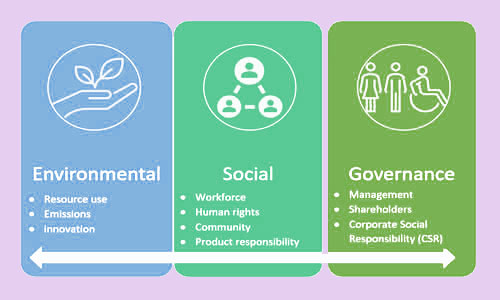


The concept of Environmental Social Governance (ESG) and the term ESG was first proposed in the 2004 UN Global Compact’s ‘Who Cares Wins’ and initiative supported by the UN Secretary General and the Global Compact in collaboration with the Swiss Government. One of the aims is to integrate environmental, social and governance criteria into financing or investment decisions, institutionalizing sustainable financing, and the consideration of ESG principles as a practice or activity that becomes a convention or norm in financial sector participants. This is driven with a positive message that ESG integration provides competitive differentiation and value creation for financial institutions that incorporate it into their strategy. As a result, many financial sector actors have now incorporated formal ESG Executive Committees into their governance structures, and report separately to stakeholders on ESG issues. Others have made ESG principles part of their drive for engagement and investing. The linkage with Financial Inclusion is that by inference, considering ESG principles and sustainable financing in their lending decisions, means that financiers need to consider the benefits not only for themselves and their clients, but the long terms benefits for society.
Environmental, Social and Governance criteria are used by socially-conscious investors and shareholders to screen investments and assess a company's impact on the world